As per the U.S Bureau of Labour Statistics, 4 million Americans quit their job in July 2021 (HBR, Sept.2021). End of July 2021 the number of open jobs was at a record high at 10.9 million. The question lies in why so many people are leaving their jobs and what can be done to understand the underlying issues and co-create a solution to retain talent.
Design thinking can be applied in various HR systems and processes in order to bring out the real employee experience wherever needed. In most organizations, HR strategy and policymaking traditionally has remained inward-looking, where the HR leaders and Business Leaders apply their contextual knowledge and understanding of the organization’s culture and people to shape up the HR strategy and policies of the organization. Many times, the actual receivers or the beneficiaries of those HR processes are not engaged or consulted in the process which creates not only challenges in its effective implementation but also misses out on addressing larger employee needs and requirements. Some of the core HR areas where the application of design thinking can provide greater employee experience and outcome are recruitment, on-boarding, talent management, performance culture-building, etc.
Employee experience has been defined in Wikipedia as a “set of psycho-cognitive sentiments about the experiential benefits of employment.” It simply means how an employee experience gets formed when an employee interacts with the organizational processes, supervisor, peers, customers, etc., and in turn, the employee develops a certain attitude or behaviour towards the career or the organization as a whole.
Design thinking as a management concept has been quite popular in the areas of marketing and product development for quite some time. However, its application in the areas of Human Resources (HR) has not been so significant though there are some organizations who have off late started applying the design thinking principles and tools to improve employee experiences. Employee experience is becoming a new area of focus for organizations in recent times and it has got further momentum during the current pandemic and the challenges imposed on organizations due to the “Great Resignation” episode. Organization and HR leaders need to continuously think about how to shape their HR practices to create a better employee experience.
Hasso-Plattner Institute of Design at Stanford prescribed a 5 steps model to implement Design Thinking :
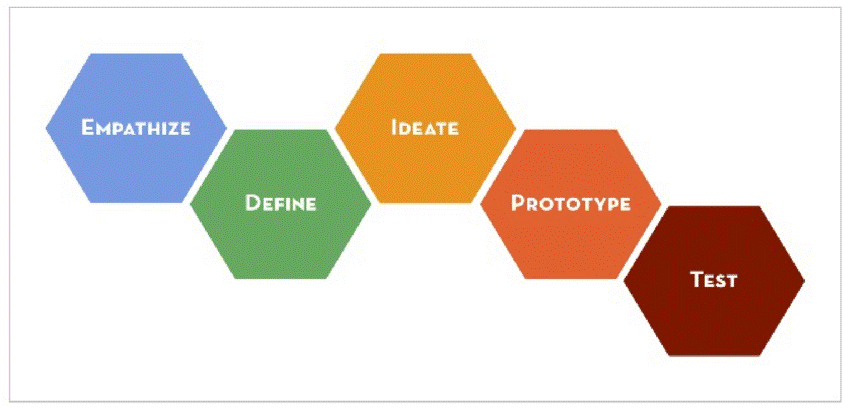
Step-I: Empathize – Design thinking process relates to how empathetic understanding can be created to understand the problem which needs to be solved. This process involves how one needs to interact with people (customers or employees or any other stakeholder in the business) to observe and understand their issues and challenges.
Step-II: Define – How do we define the problem? In this stage, all information and data received through empathize phase is analysed and synthesized in order to understand the core problem.
Step-III: Ideate – Here the project team members start generating ideas by using various ideation techniques. As the user requirements are well understood in the Empathise stage and subsequently analysed and synthesized well in the designed phase, the ideation process gets robust support.
Step-IV: Prototype – This is the experiment phase, where a scale down version of the product or services will be produced and also tested by the same team or another team in a different location to find out the best possible solution for the identified problem. This phase provides tremendous insight into how real users will view this solution.
Step-V: Test – In this final phase, the prototype solution will be rigorously tested to see how it provides the best solution to the problem. In this stage also, required alterations and refinements are made with a deep understanding of user requirements.
Considering the fact that the Design Thinking process is non-linear, the steps need not be followed in a sequential manner. Different steps can be followed at the same time by different project groups while working on a particular project or an initiative.
While design thinking has become an integral part of engineering and design discipline way back, it has also found its grounding and application in business and management. Principles of design thinking can be applied in all industries and across disciplines. In a knowledge-based VUCA (vulnerable, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous) global economy, there are waves of disruptions that are getting created by technology, geopolitics, and also pandemic like Covid. All these are continuously impacting the way business is conducted today, which in turn has a significant impact on employee morale, motivation, productivity, and organizational culture. Therefore, HR systems and processes need to be aligned and if needed re-defined with the changing business needs and employee demographics in order to attract, develop and retain the right talent for the business.
Let’s have a closer look into some of the global organizations that have applied design thinking in some of the HR practice areas in order to create a greater employee experience. CISCO was one of the first companies to recognize the potential of applying design thinking in HR areas. In 2016, CISCO launched a program called HR Hackathon to re-imagine HR solutions for its 71,000 employees globally. This led to the development of 105 new HR solutions and processes in several areas of HR like recruitment, onboarding, leadership development, talent management, etc.
Design thinking does not improve the employee experience alone, it has a direct linkage with improving customer experience also and therefore it can be a potent tool for achieving business results and outcomes. In an interview with Harvard Business Review (HBR), Dianne Gherson, IBM’s Head HR said that they could see an increase in customer satisfaction due to a higher level of employee engagement. IBM got their employees involved with HR and external experts to reimagine their Onboarding system as well as the Performance Management process to identify current issues and challenges and bring out the right solution to improve that.
Let’s have a closer look into some of the global organizations that have applied design thinking in some of the HR practice areas in order to create a greater employee experience. CISCO was one of the first companies to recognize the potential of applying design thinking in HR areas. In 2016, CISCO launched a program called HR Hackathon to re-imagine HR solutions for its 71,000 employees globally. This led to the development of 105 new HR solutions and processes in several areas of HR like recruitment, onboarding, leadership development, talent management, etc.
Design thinking does not improve the employee experience alone, it has a direct linkage with improving customer experience also and therefore it can be a potent tool for achieving business results and outcomes. In an interview with Harvard Business Review (HBR), Dianne Gherson, IBM’s Head HR said that they could see an increase in customer satisfaction due to a higher level of employee engagement. IBM got their employees involved with HR and external experts to reimagine their Onboarding system as well as the Performance Management process to identify current issues and challenges and bring out the right solution to improve that.
Pixar has got a dedicated Employee Experience Manager, who regularly holds employee conversations in order to constantly understand employee needs, requirements, experience, and gaps and provide those input in the process of making employee-centric HR interventions.
SAP has identified four critical success factors when implementing design thinking:
- Leadership: Link design thinking initiatives to your strategic goals. Provide direction, resources, and commitment.
- People: Enable champions to lead the change through successful lighthouse projects. Build up an internal design thinking community where best practices are shared.
- Process: Use the generic design thinking framework, but evolve the method and tools so they support your company’s objectives.
- Environment: Develop and create collaborative workspaces for your workforce. Focus is on how to co-innovate with your customers and partners.
Changing landscape of the business and ever-increasing challenges are leading to the need for developing a higher level of employee experience at the workplace so that it leads to high engagement as well as talent retention. HR has the opportunity to leverage the design thinking approach for co-creation purposes involving cross-functional teams which not only can lower the challenge of implementation of HR policies and programs but also create a deeper involvement of people from other functions in evolving people practices in the organization. Soft is hard now!
References
- Martin, R. (2009) The Design of Business, Harvard Business School Press.
- Liedtka, J. (2018, Sept-Oct) Why Design Thinking Works, Harvard Business Review
- SAP (2016) Design Thinking and Digital Transformation
- Kolko, J. (2015, Sep) The Evolution of Design Thinking. Harvard Business Review
- Martin, R. (2009) The Design of Business, Harvard Business School Press.
- Liedtka, J. (2018, Sept-Oct) Why Design Thinking Works, Harvard Business Review
- Kolko, J. (2015, Sep) The Evolution of Design Thinking. Harvard Business Review
- Liedtka, J.(2014) Batten Brieng: Understanding the Power of Design Thinking. Retrieved fromhttps://issuu.com/batteninstitute/docs/designthinking-121814-issue
- Deloitte Global Human Capital Trends, 2017